Sunday, October 24, 2010
Week 12 - Project Management
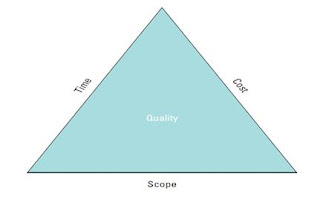
- Explain the triple constraint and its importance in project management.
The triple constraint involves making tradeoffs between scope, time and cost for a project. It is inevitable in a project life cycle that there will be changes to the scope, time or cost of the project.
These three variables are interdependent: You cannot change one without changing the others.
— Increased Scope = increased time + increased cost
— Tight Time = increased costs + reduced scope
—
2. Describe the two primary diagrams most frequently used in project planning
PERT chart – a graphical network model that depicts a project’s tasks and the relationships between those tasks : Dependency & Critical path.
Gantt chart – a simple bar chart that depicts project tasks against a calendar. A Gantt chart is one of the most common tools used by project managers.
- Identify the three primary areas a project manager must focus on managing to ensure success
- Managing people
- Managing communications
- Managing change
Managing people is one of the hardest and most critical efforts a project manager undertakes. Resolving conflicts within the team and balancing the needs of the project with the personal and professional needs of the team are two of the challenges facing project managers.
- Outline reasons why projects fail and two reasons why projects succeed.
Fail | Succeed |
— Failure to align project with organizational objectives — Poor scope — Unrealistic expectations — Lack of executive sponsorship — Lack of project management — Inability to move beyond individual and personality conflicts — Politics | — Project Sponsorship at executive level — Good project charter — Strong project management — The right mix of team players — Good decision making structure — Good communication — Team members are working toward common goals |
Click on the link below to see Week 12 Slides:
Week 10 -Customer Relationship Management & Business Intelligence
- What is your understanding of CRM?
Customer relationship management (CRM) – involves managing all aspects of a customer’s relationship with an organization/management to increase customer loyalty and retention and an organization’s profitability. CRM helps companies make the their interactions with customers seem friendlier through individualization as well as increased profits by better service.
- Compare operational and analytical customer relationship management.
Operational CRM: supports traditional transactional processing for day-to-day front-office operations or systems that deal directly with the customers. Focuses on organising and simplifying the management of customer information. It uses a database to provide consistent information about a company’s interaction with a customer.
Analytical CRM: supports back-office operations and strategic analysis and includes all systems that do not deal directly with the customers. Analytical CRM uses data mining to provide strategic data about customers to gain business. Data mining uses various modelling and analysis techniques to find patterns and relationships to make accurate predictions.
Predictions might include;
— Which customers to market to
— Up selling / Cross selling
— Retaining good customers
- Describe and differentiate the CRM technologies used by marketing departments and sales departments
Three marketing operational CRM technologies:
- List generator – compiles customer information from a variety of sources and segment the information for different marketing campaigns
- Campaign management system – guides users through marketing campaigns
- Cross-selling and up-selling
÷ Cross-selling – selling additional products or services
÷ Up-selling – increasing the value of the sale
- How could a sales department use operational CRM technologies?
The sales department could use operational CRM technologies for sales management (selling the product), contacting management and opportunity management .
- Describe business intelligence and its value to businesses
Business intelligence (BI) – applications and technologies used to gather, provide access to, and analyses data and information to support decision-making efforts. BI includes simple MS Excel Pivot tables to highly sophisticated software that fetches data from the different front-and back-office systems.
Many Businesses are finding that they must identify and meet the fast-changing needs and wants of different customer segments in order to stay competitive in today’s consumer-centric market. BI can tell companies things like;
— Determine who are the best and worst customers thereby gaining insight into where it needs to concentrate more for its future sales
— Identify exceptional sales people
— Determine whether or not campaigns have been successful
— Determine in which activity they are making or losing money.
- Explain the problem associated with business intelligence. Describe the solution to this business problem
Companies can have a lot of data; however they are not able to benefit from levering this information and turning it into useful data for analytical and strategic decision making.
The issue most organisations are facing today is that it is next to impossible to understand their own strengths and weaknesses, let alone their enemies, because the enormous amount of organisational data is inaccessible to all but the IT department. The problem: data rich, information poor .
7. What are two possible outcomes a company could get from using data mining?
Two possible outcomes companies could get from using data mining are patterns and relationships among the data. This help determine what is business is and should be doing for future practices.
Click on the link below to see Week 10 Slides:
Week 9- Operations Management and Supply Chain Management
1. Define the term operations management
Operations management (OM) is the management of systems or processes that convert or transform resources into goods and services (inputs to outputs).
2. Explain operations management’s role in business
This is a wide role that works across many divisions is business such as production and marketing. It works by adding value through:
- Forecasting (supply and demand)
- Capacity panning
- Scheduling
- Managing inventory
- Assuring quality
- Motivating and training employees
- Locating facilities
3. Describe the correlation between operations management and information technology
Managers use IT to heavily influence OM decisions including:
- What: what resources will be needed and what amounts?
- When: when should the work is scheduled?
- Where: where work performed?
- How: how will the work be done?
- Who: who will perform the work?
As well as decisions related to cogs, quality, customer service and resources needed .
4. Explain supply chain management and its role in a business
Supply chain management (SCM) involves the management of information flows between and among stages in a supply chain to maximise total supply chain effectiveness and profitability. The supply chain is a network of organisations and facilities that transform raw materials into products delivered to customers. The chain includes transportation companies, ware houses and inventories and transmitting messages and information among organisations.
5. List and describe the five components of a typical supply chain
Along with the diagram above the following chain corresponds with the appropriate steps.
Supplier – Supplies the resources/raw materials to manufacturer
Manufacturer – Makes the product/service
Distributor – Distributes the product to the retailer/sellers
Retailer – Sells the products
Customer – User and/or consumer of the products
6. Define the relationship between information technology and the supply chain.
Information technology advances in the five typical supply chain components which significantly improve companies forecasting and business operations. It also creates integrations or tight process and information linkages between functions within an organisation. It ensures good quality in the products and faster decision making .
Operations management (OM) is the management of systems or processes that convert or transform resources into goods and services (inputs to outputs).
2. Explain operations management’s role in business
This is a wide role that works across many divisions is business such as production and marketing. It works by adding value through:
- Forecasting (supply and demand)
- Capacity panning
- Scheduling
- Managing inventory
- Assuring quality
- Motivating and training employees
- Locating facilities
3. Describe the correlation between operations management and information technology
Managers use IT to heavily influence OM decisions including:
- What: what resources will be needed and what amounts?
- When: when should the work is scheduled?
- Where: where work performed?
- How: how will the work be done?
- Who: who will perform the work?
As well as decisions related to cogs, quality, customer service and resources needed .
4. Explain supply chain management and its role in a business
Supply chain management (SCM) involves the management of information flows between and among stages in a supply chain to maximise total supply chain effectiveness and profitability. The supply chain is a network of organisations and facilities that transform raw materials into products delivered to customers. The chain includes transportation companies, ware houses and inventories and transmitting messages and information among organisations.
5. List and describe the five components of a typical supply chain
Along with the diagram above the following chain corresponds with the appropriate steps.
Supplier > Manufacturer > Distribution > Retailer > Customer
Supplier – Supplies the resources/raw materials to manufacturer
Manufacturer – Makes the product/service
Distributor – Distributes the product to the retailer/sellers
Retailer – Sells the products
Customer – User and/or consumer of the products
UPSTREAM (manufacturer) -> DOWNSTREAM (retailer)
6. Define the relationship between information technology and the supply chain.
Information technology advances in the five typical supply chain components which significantly improve companies forecasting and business operations. It also creates integrations or tight process and information linkages between functions within an organisation. It ensures good quality in the products and faster decision making .
Click on the link below to see Week 9 Slides:
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)