Sunday, October 24, 2010
Week 12 - Project Management
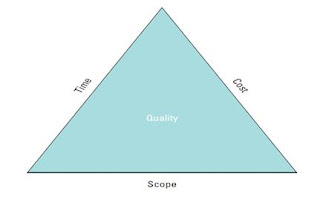
- Explain the triple constraint and its importance in project management.
The triple constraint involves making tradeoffs between scope, time and cost for a project. It is inevitable in a project life cycle that there will be changes to the scope, time or cost of the project.
These three variables are interdependent: You cannot change one without changing the others.
— Increased Scope = increased time + increased cost
— Tight Time = increased costs + reduced scope
—
2. Describe the two primary diagrams most frequently used in project planning
PERT chart – a graphical network model that depicts a project’s tasks and the relationships between those tasks : Dependency & Critical path.
Gantt chart – a simple bar chart that depicts project tasks against a calendar. A Gantt chart is one of the most common tools used by project managers.
- Identify the three primary areas a project manager must focus on managing to ensure success
- Managing people
- Managing communications
- Managing change
Managing people is one of the hardest and most critical efforts a project manager undertakes. Resolving conflicts within the team and balancing the needs of the project with the personal and professional needs of the team are two of the challenges facing project managers.
- Outline reasons why projects fail and two reasons why projects succeed.
Fail | Succeed |
— Failure to align project with organizational objectives — Poor scope — Unrealistic expectations — Lack of executive sponsorship — Lack of project management — Inability to move beyond individual and personality conflicts — Politics | — Project Sponsorship at executive level — Good project charter — Strong project management — The right mix of team players — Good decision making structure — Good communication — Team members are working toward common goals |
Click on the link below to see Week 12 Slides:
Week 10 -Customer Relationship Management & Business Intelligence
- What is your understanding of CRM?
Customer relationship management (CRM) – involves managing all aspects of a customer’s relationship with an organization/management to increase customer loyalty and retention and an organization’s profitability. CRM helps companies make the their interactions with customers seem friendlier through individualization as well as increased profits by better service.
- Compare operational and analytical customer relationship management.
Operational CRM: supports traditional transactional processing for day-to-day front-office operations or systems that deal directly with the customers. Focuses on organising and simplifying the management of customer information. It uses a database to provide consistent information about a company’s interaction with a customer.
Analytical CRM: supports back-office operations and strategic analysis and includes all systems that do not deal directly with the customers. Analytical CRM uses data mining to provide strategic data about customers to gain business. Data mining uses various modelling and analysis techniques to find patterns and relationships to make accurate predictions.
Predictions might include;
— Which customers to market to
— Up selling / Cross selling
— Retaining good customers
- Describe and differentiate the CRM technologies used by marketing departments and sales departments
Three marketing operational CRM technologies:
- List generator – compiles customer information from a variety of sources and segment the information for different marketing campaigns
- Campaign management system – guides users through marketing campaigns
- Cross-selling and up-selling
÷ Cross-selling – selling additional products or services
÷ Up-selling – increasing the value of the sale
- How could a sales department use operational CRM technologies?
The sales department could use operational CRM technologies for sales management (selling the product), contacting management and opportunity management .
- Describe business intelligence and its value to businesses
Business intelligence (BI) – applications and technologies used to gather, provide access to, and analyses data and information to support decision-making efforts. BI includes simple MS Excel Pivot tables to highly sophisticated software that fetches data from the different front-and back-office systems.
Many Businesses are finding that they must identify and meet the fast-changing needs and wants of different customer segments in order to stay competitive in today’s consumer-centric market. BI can tell companies things like;
— Determine who are the best and worst customers thereby gaining insight into where it needs to concentrate more for its future sales
— Identify exceptional sales people
— Determine whether or not campaigns have been successful
— Determine in which activity they are making or losing money.
- Explain the problem associated with business intelligence. Describe the solution to this business problem
Companies can have a lot of data; however they are not able to benefit from levering this information and turning it into useful data for analytical and strategic decision making.
The issue most organisations are facing today is that it is next to impossible to understand their own strengths and weaknesses, let alone their enemies, because the enormous amount of organisational data is inaccessible to all but the IT department. The problem: data rich, information poor .
7. What are two possible outcomes a company could get from using data mining?
Two possible outcomes companies could get from using data mining are patterns and relationships among the data. This help determine what is business is and should be doing for future practices.
Click on the link below to see Week 10 Slides:
Week 9- Operations Management and Supply Chain Management
1. Define the term operations management
Operations management (OM) is the management of systems or processes that convert or transform resources into goods and services (inputs to outputs).
2. Explain operations management’s role in business
This is a wide role that works across many divisions is business such as production and marketing. It works by adding value through:
- Forecasting (supply and demand)
- Capacity panning
- Scheduling
- Managing inventory
- Assuring quality
- Motivating and training employees
- Locating facilities
3. Describe the correlation between operations management and information technology
Managers use IT to heavily influence OM decisions including:
- What: what resources will be needed and what amounts?
- When: when should the work is scheduled?
- Where: where work performed?
- How: how will the work be done?
- Who: who will perform the work?
As well as decisions related to cogs, quality, customer service and resources needed .
4. Explain supply chain management and its role in a business
Supply chain management (SCM) involves the management of information flows between and among stages in a supply chain to maximise total supply chain effectiveness and profitability. The supply chain is a network of organisations and facilities that transform raw materials into products delivered to customers. The chain includes transportation companies, ware houses and inventories and transmitting messages and information among organisations.
5. List and describe the five components of a typical supply chain
Along with the diagram above the following chain corresponds with the appropriate steps.
Supplier – Supplies the resources/raw materials to manufacturer
Manufacturer – Makes the product/service
Distributor – Distributes the product to the retailer/sellers
Retailer – Sells the products
Customer – User and/or consumer of the products
6. Define the relationship between information technology and the supply chain.
Information technology advances in the five typical supply chain components which significantly improve companies forecasting and business operations. It also creates integrations or tight process and information linkages between functions within an organisation. It ensures good quality in the products and faster decision making .
Operations management (OM) is the management of systems or processes that convert or transform resources into goods and services (inputs to outputs).
2. Explain operations management’s role in business
This is a wide role that works across many divisions is business such as production and marketing. It works by adding value through:
- Forecasting (supply and demand)
- Capacity panning
- Scheduling
- Managing inventory
- Assuring quality
- Motivating and training employees
- Locating facilities
3. Describe the correlation between operations management and information technology
Managers use IT to heavily influence OM decisions including:
- What: what resources will be needed and what amounts?
- When: when should the work is scheduled?
- Where: where work performed?
- How: how will the work be done?
- Who: who will perform the work?
As well as decisions related to cogs, quality, customer service and resources needed .
4. Explain supply chain management and its role in a business
Supply chain management (SCM) involves the management of information flows between and among stages in a supply chain to maximise total supply chain effectiveness and profitability. The supply chain is a network of organisations and facilities that transform raw materials into products delivered to customers. The chain includes transportation companies, ware houses and inventories and transmitting messages and information among organisations.
5. List and describe the five components of a typical supply chain
Along with the diagram above the following chain corresponds with the appropriate steps.
Supplier > Manufacturer > Distribution > Retailer > Customer
Supplier – Supplies the resources/raw materials to manufacturer
Manufacturer – Makes the product/service
Distributor – Distributes the product to the retailer/sellers
Retailer – Sells the products
Customer – User and/or consumer of the products
UPSTREAM (manufacturer) -> DOWNSTREAM (retailer)
6. Define the relationship between information technology and the supply chain.
Information technology advances in the five typical supply chain components which significantly improve companies forecasting and business operations. It also creates integrations or tight process and information linkages between functions within an organisation. It ensures good quality in the products and faster decision making .
Click on the link below to see Week 9 Slides:
Friday, September 24, 2010
Week 8- Networks, Telecommunications and Mobile Technology
Explain the business benefits of using wireless technology.
Wireless technology allows us to get information anywhere and on the run. It increases productivity and lets us receive live data which is very convenient .It is universal which benefits a businesses ecommerce as well as allowing businesses to have mass customisation.
Describe the business benefits associated with VoIP
The benefits include telecommunications via phone calls over the internet which is a major cost cut for businesses as well multimedia cost cuts. It is also used for video conferencing and gives managers a greater span of control. It saves money as VOIP runs over the existing computer network, calls over the net do not attract telecommunication charges and customers can port their numbers between carriers.
Compare LANs and WANs
LANS are local area networks , in one geographical area for example Uni.
WANS are wide area networks which connect computers at different geographical sites.
Describe RFID and how it can be used to help make a supply chain more effective.
RFID = Radio Frequency Identification , is the tags that use radio waves to transmit data .It can be used in things such as inventory , passports and transportation . It makes the supply chain more effective by heavily tracking the inventory of businesses.
Identify the advantages and disadvantage of deploying mobile technology
Advantages would include the convenience, efficiency, accuracy, consistency etc. of the transfer of data for both personal and business uses. There are no disadvantages apart from the inappropriate use of mobile phone cameras.
Wireless technology allows us to get information anywhere and on the run. It increases productivity and lets us receive live data which is very convenient .It is universal which benefits a businesses ecommerce as well as allowing businesses to have mass customisation.
Describe the business benefits associated with VoIP
The benefits include telecommunications via phone calls over the internet which is a major cost cut for businesses as well multimedia cost cuts. It is also used for video conferencing and gives managers a greater span of control. It saves money as VOIP runs over the existing computer network, calls over the net do not attract telecommunication charges and customers can port their numbers between carriers.
Compare LANs and WANs
LANS are local area networks , in one geographical area for example Uni.
WANS are wide area networks which connect computers at different geographical sites.
Describe RFID and how it can be used to help make a supply chain more effective.
RFID = Radio Frequency Identification , is the tags that use radio waves to transmit data .It can be used in things such as inventory , passports and transportation . It makes the supply chain more effective by heavily tracking the inventory of businesses.
Identify the advantages and disadvantage of deploying mobile technology
Advantages would include the convenience, efficiency, accuracy, consistency etc. of the transfer of data for both personal and business uses. There are no disadvantages apart from the inappropriate use of mobile phone cameras.
Click here for Week 8 Slides:
Week 7- Databases and Data Warehouses
List, describe, and provide an example of each of the five characteristics of high quality information. (Characteristic ,Describe, Example)
Accuracy - Are all the values correct? Is the name spelt correctly? Is the dollar amount recorded properly?
Completeness- Are any of the values missing? Is the address complete including street, city, state and zip code?
Consistency - Is aggregate or summary information n agreement with detailed information? Do all total fields equal the true total of the individual fields?
Uniqueness - In each transaction, entity and event represented only once in the information? Are there any duplicate customers?
Timelines - Is the information current with respect to the business requirements? Is the information updated weekly, daily or hourly?
Define the relationship between a database and a database management system.
Database : maintains information about various types of objects (inventory), events (transactions), people (employees) and places (warehouses).
Database management system (DBMS) : is software through which users and application programs interact with a database . Think of it this way: A DBMS is to a database as word processing software is to a document or as a spreadsheet software is to a spreadsheet. Its primary task is to allow users to create access and use information stored in a database.
Describe the advantages an organisation can gain by using a database.
Increased flexibility: data bases tend a mirror business structures and a good data base can handle changes quickly and easily, just as any good business needs to be able to handle changes quickly and easily. Data bases provide flexibility in allowing each user to access the formation in whatever way best suits his or her needs.
Physical view : information deals with the physical storage of information on a storage device such as a hard disk
The logical view: of information focuses on how users logically access information to meet their particular business needs.
Increased scalability and performances: Scalability refers to how well a system can adapt to increased demands. Performance measures how quickly a system performs a certain process or transaction.
Reduced redundancy: redundancy is the duplication of information, or storing the same information in multiple places. Redundant information occurs because organisations frequently capture and store the same information in multiple locations
Increased integrity (quality): in a measure of the quality of information. Within a database environment, integrity constraints are rules that help ensure the quality of information. Integrity constraints are defined and built into the data base.
Increased security: as system become increasingly complex and more available over the internet, security becomes an even bigger issue. Data bases offer many security features including : passwords, access levels and access controls
Define the fundamental concepts of the relational database model.
Table : a set of relation records
Record: a collection of data about an individual item
Field: a single item of data common to all records
Describe the benefits of a data-driven website.
-Development of a business
-Content management
-Future expandability
-Minimising human error
-Cutting production and update costs
-More efficient
-Improved stability
Describe the roles and purposes of data warehouses and data mining in an organisation
Data warehouses are a logical collection of information gathered from many different operational databases that support business analysis activities and decision making tasks. It main purpose is to aggregate information throughout an organisation into a single repository for decision making purposes.
Data mining is the process of analysing data to extract information not offered by the raw data alone to perform users need data mining tools such as cluster analysis , association detection and statistical analysis .
Accuracy - Are all the values correct? Is the name spelt correctly? Is the dollar amount recorded properly?
Completeness- Are any of the values missing? Is the address complete including street, city, state and zip code?
Consistency - Is aggregate or summary information n agreement with detailed information? Do all total fields equal the true total of the individual fields?
Uniqueness - In each transaction, entity and event represented only once in the information? Are there any duplicate customers?
Timelines - Is the information current with respect to the business requirements? Is the information updated weekly, daily or hourly?
Define the relationship between a database and a database management system.
Database : maintains information about various types of objects (inventory), events (transactions), people (employees) and places (warehouses).
Database management system (DBMS) : is software through which users and application programs interact with a database . Think of it this way: A DBMS is to a database as word processing software is to a document or as a spreadsheet software is to a spreadsheet. Its primary task is to allow users to create access and use information stored in a database.
Describe the advantages an organisation can gain by using a database.
Increased flexibility: data bases tend a mirror business structures and a good data base can handle changes quickly and easily, just as any good business needs to be able to handle changes quickly and easily. Data bases provide flexibility in allowing each user to access the formation in whatever way best suits his or her needs.
Physical view : information deals with the physical storage of information on a storage device such as a hard disk
The logical view: of information focuses on how users logically access information to meet their particular business needs.
Increased scalability and performances: Scalability refers to how well a system can adapt to increased demands. Performance measures how quickly a system performs a certain process or transaction.
Reduced redundancy: redundancy is the duplication of information, or storing the same information in multiple places. Redundant information occurs because organisations frequently capture and store the same information in multiple locations
Increased integrity (quality): in a measure of the quality of information. Within a database environment, integrity constraints are rules that help ensure the quality of information. Integrity constraints are defined and built into the data base.
Increased security: as system become increasingly complex and more available over the internet, security becomes an even bigger issue. Data bases offer many security features including : passwords, access levels and access controls
Define the fundamental concepts of the relational database model.
Table : a set of relation records
Record: a collection of data about an individual item
Field: a single item of data common to all records
Describe the benefits of a data-driven website.
-Development of a business
-Content management
-Future expandability
-Minimising human error
-Cutting production and update costs
-More efficient
-Improved stability
Describe the roles and purposes of data warehouses and data mining in an organisation
Data warehouses are a logical collection of information gathered from many different operational databases that support business analysis activities and decision making tasks. It main purpose is to aggregate information throughout an organisation into a single repository for decision making purposes.
Data mining is the process of analysing data to extract information not offered by the raw data alone to perform users need data mining tools such as cluster analysis , association detection and statistical analysis .
Click here to see Week 7 Slides:
Week 6- Enterprise Architectures
What is information architecture and what is information infrastructure and how do they differ and how do they relate to each other?
Information architecture: identifies where and how important information, like customer records, is maintained and secured. A single backup or restore failure can cost an organisation more than time and memory; some data cannot be recreated and the business intelligence lost from that data can be tremendous. Three primary areas an enterprises should focus on :
-Backup & recovery
-Disaster recovery
-Information security
Information infrastructure: includes hardware, software, services and people that when combined provide the underlying foundation to support the organisations goals.
Describe how an organisation can implement a solid information architecture
An organisation can implement a solid information architecture by having a strong information security plan, managing user access and having up to date antivirus software and patched.
List and describe the five requirement characteristics of infrastructure architecture.
Infrastructure architecture includes hardware, software and telecommunications equipment that, when combined, provide the underlying foundation to support the organisations goals.
- Flexibility: systems must be flexible enough to meet all types of business changes. E.g. changing currencies, languages.
- Scalability: how well a system can adapt to increased demands. A number of factors can create organisational growth including market growth including marketing, industry and economy factors.
- Reliability: ensures all systems are functioning correctly and providing accurate information. Reliability in another term for accuracy when discussing the correctness of systems within the context of efficiency IT metrics.
- Availability: (Efficiency IT metrics) addresses when systems can be accessed by users. High availability refers to a system or component that is continuously operational for a desirably long length of time. It typically measured relative to 100% operational or never failing.
- Performance: measures how quickly a system performs a certain process or transaction (in terms of efficiency IT metrics of both speed and throughput). Not having enough performance capacity can have a devastating, negative impact on a business.
Describe the business value in deploying a service oriented architecture
It ensures that IT systems can adapt quickly, easily and economically to support rapidly changing business needs. By using meta data and existing applications, users can re use applications/services many times for different tasks, making development cheaper and more flexible.
What is an event?
Events are the eyes and ears of the business expressed in technology – they detect threats and opportunities and alert those who can act on the information. Pioneers by telecommunication mad financial services companies , this involves using IT systems to monitor a business process for events that mater – a stock out in the warehouse or an especially large charge on a customer’s credit card and automatically alert the people best equipped to handle the issue.
What is a service?
Services are more like software products than they are coding projects. They must appeal to a broad audience and they need to be reusable if they are going to have an impact on productivity. Early forms of services were defined at too low a low level in the architecture to interest the business, such as simple print and save services.
What emerging technologies can companies can use to increase performance and utilise their infrastructure more effectively?
-Interoperability
-eXtensible Markup Language
-Loose Coupling
-Virtualisation
-Grid Computing
Information architecture: identifies where and how important information, like customer records, is maintained and secured. A single backup or restore failure can cost an organisation more than time and memory; some data cannot be recreated and the business intelligence lost from that data can be tremendous. Three primary areas an enterprises should focus on :
-Backup & recovery
-Disaster recovery
-Information security
Information infrastructure: includes hardware, software, services and people that when combined provide the underlying foundation to support the organisations goals.
Describe how an organisation can implement a solid information architecture
An organisation can implement a solid information architecture by having a strong information security plan, managing user access and having up to date antivirus software and patched.
List and describe the five requirement characteristics of infrastructure architecture.
Infrastructure architecture includes hardware, software and telecommunications equipment that, when combined, provide the underlying foundation to support the organisations goals.
- Flexibility: systems must be flexible enough to meet all types of business changes. E.g. changing currencies, languages.
- Scalability: how well a system can adapt to increased demands. A number of factors can create organisational growth including market growth including marketing, industry and economy factors.
- Reliability: ensures all systems are functioning correctly and providing accurate information. Reliability in another term for accuracy when discussing the correctness of systems within the context of efficiency IT metrics.
- Availability: (Efficiency IT metrics) addresses when systems can be accessed by users. High availability refers to a system or component that is continuously operational for a desirably long length of time. It typically measured relative to 100% operational or never failing.
- Performance: measures how quickly a system performs a certain process or transaction (in terms of efficiency IT metrics of both speed and throughput). Not having enough performance capacity can have a devastating, negative impact on a business.
Describe the business value in deploying a service oriented architecture
It ensures that IT systems can adapt quickly, easily and economically to support rapidly changing business needs. By using meta data and existing applications, users can re use applications/services many times for different tasks, making development cheaper and more flexible.
What is an event?
Events are the eyes and ears of the business expressed in technology – they detect threats and opportunities and alert those who can act on the information. Pioneers by telecommunication mad financial services companies , this involves using IT systems to monitor a business process for events that mater – a stock out in the warehouse or an especially large charge on a customer’s credit card and automatically alert the people best equipped to handle the issue.
What is a service?
Services are more like software products than they are coding projects. They must appeal to a broad audience and they need to be reusable if they are going to have an impact on productivity. Early forms of services were defined at too low a low level in the architecture to interest the business, such as simple print and save services.
What emerging technologies can companies can use to increase performance and utilise their infrastructure more effectively?
-Interoperability
-eXtensible Markup Language
-Loose Coupling
-Virtualisation
-Grid Computing
Click here to see Week 6 slides:
https://blackboard.nd.edu.au/webapps/portal/frameset.jsp?tab_id=_2_1&url=%2Fwebapps%2Fblackboard%2Fexecute%2Flauncher%3Ftype%3DCourse%26id%3D_127488_1%26url%3D
Week 5- Ethics and Information Security
Explain the ethical issues surrounding information technology. Intellectual property Intangible creative work that is embodied in physical item.
Copyright - The legal protection afforded an expression of an idea, such as a song, video game and some proprietary documents.
Fair-Use doctrine In certain situations, it is legal to use copyrighted material.
Pirated software- The unauthorised use, duplication, distribution or sale of copyrighted software.
Counterfeit software - Software that is manufactured to look like the real thing and sold as such.
Describe a situation involving technology that is ethical but illegal.
You make two copies of a software pacage your purchased and sell a copy to your friend. It is ethical that the software was purchased but illegal where it was copied and sold to a friend.
Describe and explain one of the computer use policies that a company might employee.
A company might employee the ethical computer policy which contains the general priciples to guide computer user behaviour .It follows by:
What are the 5 main technology security risks?
- Human error
- Natual disasters
- Technical failures
- Deliberate acts
- Management failure
Outline one way to reduce each risk.
- Human error : adequate training
- Natural disasters : regular back up procedures
- Technical failures :regular back up procedures
- Deliberate acts: passwords ,security & firewalls
- Management failure: system audits
What is a disaster recovery plan, what strategies might a firm employee?
A disaster recovery plan is the process of regaining access to computer systems and data after a disaster has taken place. The plan includes things like a communication plan, alternative sites, business continuity and location of back up data.
Copyright - The legal protection afforded an expression of an idea, such as a song, video game and some proprietary documents.
Fair-Use doctrine In certain situations, it is legal to use copyrighted material.
Pirated software- The unauthorised use, duplication, distribution or sale of copyrighted software.
Counterfeit software - Software that is manufactured to look like the real thing and sold as such.
Describe a situation involving technology that is ethical but illegal.
You make two copies of a software pacage your purchased and sell a copy to your friend. It is ethical that the software was purchased but illegal where it was copied and sold to a friend.
Describe and explain one of the computer use policies that a company might employee.
A company might employee the ethical computer policy which contains the general priciples to guide computer user behaviour .It follows by:
What are the 5 main technology security risks?
- Human error
- Natual disasters
- Technical failures
- Deliberate acts
- Management failure
Outline one way to reduce each risk.
- Human error : adequate training
- Natural disasters : regular back up procedures
- Technical failures :regular back up procedures
- Deliberate acts: passwords ,security & firewalls
- Management failure: system audits
What is a disaster recovery plan, what strategies might a firm employee?
A disaster recovery plan is the process of regaining access to computer systems and data after a disaster has taken place. The plan includes things like a communication plan, alternative sites, business continuity and location of back up data.
Click here to see Week 5 Slides:
Week 4 – E business
What is an IP Address? What is its main function?
IP (internet protocol) is the basic communication language or protocol of the internet. It can also be used as a communications protocol in a private network. Each computer on the internet has its own IP address; these can be public or private however each is unique. Domain Name System is used to translate a url into an IP address. Every web address has an IP address.
What is Web 2.0, how does it differ from 1.0?
Web 1.0 – one way information, no interaction & passive
Web 2.0 - is live web. Users can collaborate and build their own content. Its involves social networking, collaboration, user build contact, user can update, create and edit, business opportunities and content, interactive. Businesses use it to enable access to critical business application for employees and customers Examples include Facebook, MySpace , Flicka etc. The Government New Grocery Watch is a good example of web 2.0 being used effectively.
What is Web 3.0?
Web 3.0 uses the concept of tagging to build information about you, your devises talk to each or and build intelligence about you. Web 3.0 is semantic web encompasses the following:
- Transforming the web into a data base
-An evolutionary path to artificial intelligence
-Search for information using different media
- Evolution towards 3D
-Data basing internet
-Tags (on video & photos)
-Build data base
-Search for media
What is eBusiness, how does it differ from eCommerce?
eBusiness is the conduction of business on the internet including, not only buying and selling but also serving customers and collaborating with business partners. eCommerce is the buying and selling of goods and services over the internet.
What is pure and partial eCommerce?
Pure eCommerce is business that operates on the internet only without any physical store e.g. Amazon.com. Partial eCommerce is business that is primarily done in the physical world although some ecommerce activities are conducted .
List and describe the various eBusiness models?
List and describe the major B2B models?
- Sell-side: Emarketplace -niche web based marketplace which one compnay sells to mnay business buyers from online catologs or auctions . eProcurment : electronic acquistion of goods and services for organisations which enables employees to buy directly for suppliers.
- Buy-side : corportae based acquisition site that uses reverse auctions , negotiations, group purchasing or any other e-procurement method .
- Electronic exchange
- Collaborative commerce
Outline 2 opportunities and 2 challenges faced by companies doing business online?
Opportunities: Growth of the business for example an international base & exposure to a wider audience/ potential customers.
Challenges: IT problems such as technical failures or computer crashing and a lot of competition/other websites.
IP (internet protocol) is the basic communication language or protocol of the internet. It can also be used as a communications protocol in a private network. Each computer on the internet has its own IP address; these can be public or private however each is unique. Domain Name System is used to translate a url into an IP address. Every web address has an IP address.
What is Web 2.0, how does it differ from 1.0?
Web 1.0 – one way information, no interaction & passive
Web 2.0 - is live web. Users can collaborate and build their own content. Its involves social networking, collaboration, user build contact, user can update, create and edit, business opportunities and content, interactive. Businesses use it to enable access to critical business application for employees and customers Examples include Facebook, MySpace , Flicka etc. The Government New Grocery Watch is a good example of web 2.0 being used effectively.
What is Web 3.0?
Web 3.0 uses the concept of tagging to build information about you, your devises talk to each or and build intelligence about you. Web 3.0 is semantic web encompasses the following:
- Transforming the web into a data base
-An evolutionary path to artificial intelligence
-Search for information using different media
- Evolution towards 3D
-Data basing internet
-Tags (on video & photos)
-Build data base
-Search for media
What is eBusiness, how does it differ from eCommerce?
eBusiness is the conduction of business on the internet including, not only buying and selling but also serving customers and collaborating with business partners. eCommerce is the buying and selling of goods and services over the internet.
What is pure and partial eCommerce?
Pure eCommerce is business that operates on the internet only without any physical store e.g. Amazon.com. Partial eCommerce is business that is primarily done in the physical world although some ecommerce activities are conducted .
List and describe the various eBusiness models?
List and describe the major B2B models?
- Sell-side: Emarketplace -niche web based marketplace which one compnay sells to mnay business buyers from online catologs or auctions . eProcurment : electronic acquistion of goods and services for organisations which enables employees to buy directly for suppliers.
- Buy-side : corportae based acquisition site that uses reverse auctions , negotiations, group purchasing or any other e-procurement method .
- Electronic exchange
- Collaborative commerce
Outline 2 opportunities and 2 challenges faced by companies doing business online?
Opportunities: Growth of the business for example an international base & exposure to a wider audience/ potential customers.
Challenges: IT problems such as technical failures or computer crashing and a lot of competition/other websites.
Click here to see Week 4 slides:
Week 3 – Strategic Decision Making
Define TPS & DSS, and explain how an organisation can use these systems to make decisions and gain competitive advantages
TPS (transaction processing system) is the basic business system that serves the operational level (analysts) in an organisation. The most common example is a payroll system or an order-entry system.
DSS (decision support system) such as Boston Coach’s, models information to support managers and business professionals during the decision making process. The three quantitative models often used by DSS are:
1) Sensitivity analysis
2) What-if analysis
3) Goal seeking analysis
Describe the three quantitative models typically used by decision support systems.
a. Sensitivity analysis –study of the impact that changes in one or more parts of a model .Users change the value of one variable repeatedly and observe the resulting changes in other variables.
b. What-if analysis- checks the impact of a change in an assumption on the proposed solutions. Users repeat this analysis until they understand all the effects of various situations.
c. Goal seeking analysis – finds the inputs necessary to achieve a goal such as a desired level of output. Instead of observing how changes in a variable affects other variables as in what if analysis , goal seeking sets a target value (a goal) for a variable and then repeatedly changes other variables until the target value is achieved .
Describe a business processes and their importance to an organisation.
A business process is a standardised set of activities that accomplish a specific task such as processing a customer’s order. It is important as it organises, coordinates and focuses on the work which is used to produce a valuable product or service for an organisation.
Compare business process improvement (BPI) and business process re-engineering (BPR).
BPI is the continual process which attempts to understand and measure the current process and make performance improvements accordingly. BPR is the analysis and redesign of workflow within and between enterprises. The purpose is to make all business processes best in class. It is through technology that it aims to support and develop theses business processes.
Describe the importance of business process modelling (or mapping) and business process models.
Business process modelling is the activity of making detailed flowcharts or process map of a work process which aims to show process details in a gradual and controlled manner, encourage consciousness and accuracy in describing the process model, focus attention on the process model interfaces and provide a powerful process analysis and consistent design vocabulary. The business process models make the processes visible.
TPS (transaction processing system) is the basic business system that serves the operational level (analysts) in an organisation. The most common example is a payroll system or an order-entry system.
DSS (decision support system) such as Boston Coach’s, models information to support managers and business professionals during the decision making process. The three quantitative models often used by DSS are:
1) Sensitivity analysis
2) What-if analysis
3) Goal seeking analysis
Describe the three quantitative models typically used by decision support systems.
a. Sensitivity analysis –study of the impact that changes in one or more parts of a model .Users change the value of one variable repeatedly and observe the resulting changes in other variables.
b. What-if analysis- checks the impact of a change in an assumption on the proposed solutions. Users repeat this analysis until they understand all the effects of various situations.
c. Goal seeking analysis – finds the inputs necessary to achieve a goal such as a desired level of output. Instead of observing how changes in a variable affects other variables as in what if analysis , goal seeking sets a target value (a goal) for a variable and then repeatedly changes other variables until the target value is achieved .
Describe a business processes and their importance to an organisation.
A business process is a standardised set of activities that accomplish a specific task such as processing a customer’s order. It is important as it organises, coordinates and focuses on the work which is used to produce a valuable product or service for an organisation.
Compare business process improvement (BPI) and business process re-engineering (BPR).
BPI is the continual process which attempts to understand and measure the current process and make performance improvements accordingly. BPR is the analysis and redesign of workflow within and between enterprises. The purpose is to make all business processes best in class. It is through technology that it aims to support and develop theses business processes.
Describe the importance of business process modelling (or mapping) and business process models.
Business process modelling is the activity of making detailed flowcharts or process map of a work process which aims to show process details in a gradual and controlled manner, encourage consciousness and accuracy in describing the process model, focus attention on the process model interfaces and provide a powerful process analysis and consistent design vocabulary. The business process models make the processes visible.
Click here to see Week 3 slides:
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)